Restraining orders are generally issued in cases involving crimes such as harassment, sexual assault, and domestic violence cases.
There are a few types of restraining orders, one of which can be issued by a judge, and each of them may remain in effect for a certain period of time.
Understanding how long do restraining orders last is crucial if you’re a ‘restrained person’, as you can face serious consequences if you violate a restraining order.
Lets discuss some general information about restraining orders, their common types, what they contain, how long restraining orders last, and what’s required to get a restraining order.
Table of Contents
Understanding Restraining Orders
A restraining order, also referred to as a ‘protective order’ or emergency protective order is a court order that safeguards someone from being sexually or physically abused, harassed, threatened, or stalked.
The person obtaining the restraining order is called the ‘protected person’.
The person against whom the restraining order is given is the ‘restrained person’. Sometimes, restraining orders include some other ‘protected persons’ such as household or family members of the protected person.
 A plaintiff may ask the court for the issuance of a restraining order on anyone they feel imminent danger and present danger to prevent such a person from performing a dangerous act.
A plaintiff may ask the court for the issuance of a restraining order on anyone they feel imminent danger and present danger to prevent such a person from performing a dangerous act.
Related Study: How To Get A Debt Lawsuit Dismissed
It is believed that the court in order to decide a restraining order likley to consider following conditions: -
- Whether the complainant will suffer an irremediable injury if the court doesn’t grant the order.
- Whether the plaintiff is expected to succeed in their request based on the case’s merits.
- Whether the defendant will get harmed more than the plaintiff is helped.
- Whether granting the restraining order is in the public interest.
- If the criteria above are met and the court justifies the restraining order, it’ll grant the complainant’s request and serve the defendant with a restraining order.
Types of Restraining Orders
There are FOUR main types of the restraining orders you can ask for: -
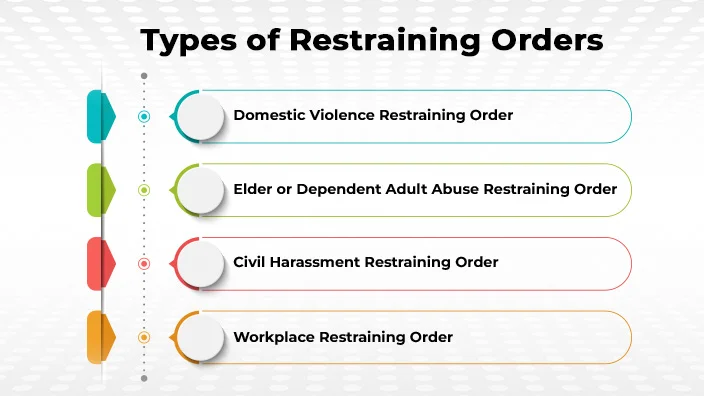
Domestic Violence Restraining Order
You can request a restraining order if: -
- You’ve been abused by someone, and
- You have a close relationship with that very person (married or registered domestic partner, separated, divorced, dating, have a child together, or live together or used to live together- but more than roommates), or you’re closely related (child, parent, sister, brother, grandmother, grandfather, in-law).
Elder Abuse Restraining Order
For further abuse, you can request an elder or dependent abuse order if: -
- You’re 65 years old, or older, or
- You’re between 18 and 64 and have certain physical or mental disabilities that restrain you from being able to perform normal activities or protect yourself, and
You’re a victim of: -
- Neglect or abandonment,
- Child abuse
- Physical or financial abuse,
- Treatment that has mentally or physically hurt you, or
- Deprivation by a guardian of basic things or services you need won’t suffer mentally, emotionally, or physically.
Civil Harassment Restraining Order
You can request a civil harassment restraining order if you’re being abused, harassed, stalked, or threatened by a person you’re not as close.
Likewise, it can be got in cases of domestic violence cases, such as a neighbor, a roommate, or more distant family members like aunts and uncles, cousins, or nieces or nephews.
Workplace Restraining Order
You can request for a workplace restraining order if: -

- You’re an employer, and
- You request a restraining order for the immediate protection of an employee who has suffered serious harassment, stalking, repeat violence, or a credible threat of violence at the workplace.
- An employee cannot request a workplace restraining order.
If the employee wants to protect herself/himself, he or she can request a civil harassment restraining order (or domestic violence restraining order if the abuser is a spouse, or former spouse, or a close family member).
Who Can Receive a Restraining Order?
Courts issue restraining orders for various reasons. The most common parties who will get a restraining order include: -
- Domestic abusers
- Stalkers
- Harassers
- Employers or employees threatening to reveal sensitive information
- Someone who is infringing on another person’s copyrights.
The most common reason for giving a restraining order is to guard women and children from people who are abusing, harassing, or stalking them.
No matter which state issues a restraining order, the restrained person must respect the order in all U.S. territories and states.
Restraining Orders Lasting Period
How long a restraining order lasts will depend on certain circumstances of the order. In cases of employment disputes or copyright infringements, temporary restraining orders are for a short period.
If you’re dealing with a restraining temporary order for a labor dispute, the law sets a 5-day limit. On the other hand, a restraining order for copyright infringement usually lasts only until the parties settle their issues.
 However, if a restraining order is granted to prevent domestic abuse, harassment, or stalking, it’ll last longer up to five years. Generally, a restraining will last up to two years.
However, if a restraining order is granted to prevent domestic abuse, harassment, or stalking, it’ll last longer up to five years. Generally, a restraining will last up to two years.
The court may extend that period but they must put forth evidence that this is essential to protect the complainant.
If a victim wants to apply again for another restraining order once the first order expires, they can do so.
They must affirm the continued threat as per the information and evidence they stated in the first restraining order application.
What is Required to Get a Restraining Order?
The court requires evidence for the issuance of a restraining order. Within 20 days of the initial application for an initial order, a hearing will be held by the court to examine the shreds of evidence for a restraining order.
The application must include a detailed account of the threat to the individual, including what they’ve experienced and the possibility of experiencing it in the future.
Besides permanent restraining orders, the applicant may also request a temporary ex parte injunction that effect immediately, and is formed to protect the family while they wait for a full hearing and a permanent order. An ex parte order doesn’t exceed 20 days.
What Actions Do Restraining Orders Prevent?
Generally, restraining orders can include the following civil actions: -
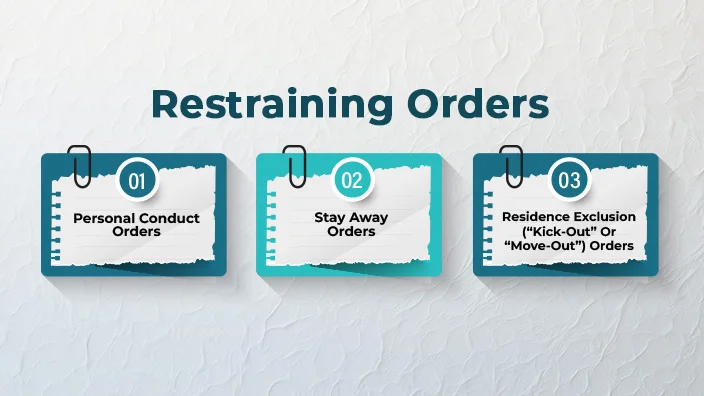
Personal Conduct Orders
Personal conduct orders are to stop against a person or persons named in the restraining order as a ‘protected person’. Some of the things or acts that a restrained person can be ordered to stop are: -
- Calling, contacting, or sending any messages (including e-mails)
- Striking, attacking, or battering
- Threatening
- Stalking
- Harassing
- Sexual violence
- Dating Violence
- Destroying personal property; or
- Disturbing the peace of the protected persons.
Stay Away Orders
Stay away orders are to keep the ‘restrained person’ a certain distance (like 100 yards) away from: -
- The protected person or persons
- Where protected persons live
- Their place of work
- Their children’s childcare places or schools
- Their vehicle
- Any other important places where they go.
Residence Exclusion (Kick-Out) Orders
In these orders, the ‘restrained person’ is directed to move out from where the ‘protected person’ lives, taking only the clothing and personal belongings till the court hearing.
These orders can only be requested in cases of domestic violence or elder or dependent restraining orders.
Restraining orders can have serious legal consequences and legal implications for the person to be restrained, which may include: -

- They won’t be able to do certain things or go to certain places.
- They might have to move out of their home.
- It may affect their ability to meet or see their children.
- They won’t be generally able to own a gun, (and will have to turn in, store, or sell any guns they have then, and won’t be able to buy a gun while a restraining order is in effect).
- It may affect their immigration status if they’re trying to get a green card or visa.
If the ‘restrained person’ breaks the restraining order, they may pay a fine, go for jail time, or both.
Conclusion
how long do restraining orders last? How long a restraining order remains in effect will depend on the circumstances and type of the order. They can either be short-term or long term restraining orders.
Courts issue restraining orders for various reasons and those getting a restraining order may include stalkers, harassers, domestic abusers, someone infringing on another person’s copyrights, etc.
The reason for giving a restraining order is commonly to protect children and women from people who are abusing, harassing, or stalking them, and the people who have restraining orders can face serious consequences for it. In case of violating a restraining order, they may pay a fine, go to jail, or both.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Florida restraining order work?
Unless the court order speaks otherwise, this means no contact in person, by text messages, phone, e-mail, letter, or any other method.
How long is a no contact order good for in Florida?
If the Florida court decides that a no-contact order is appropriate, it’ll likely issue a short-term ex parte injunction, which will remain in effect for 15 days.
Can I fight a restraining order in California?
Your abuser, the ‘restrained person’ can hire a criminal defense attorney in order to challenge the order at the permanent restraining order hearing. These hearings generally occur for about 21 days.
Can you buy a gun if you have a restraining order in California?
The person who has a restraining order in California can’t have or own a firearm, firearm parts, or ammunition.